Otorrhea
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is Otorrhea ?
Otorrhea can be symptoms of various issues all of which could be life threatening. In this article, we will discuss the possible causes, treatments and risk factors of otorrhea.
Also briefly it will briefly describe the definition or meaning of otorrhea as well as a quick review of the ears anatomy. This article is medical based but should not take the place of medical counsel. It should be noted that in any case of otorrhea medical attention is necessary.
The actual breakdown of the word torches specifically means runny ear. Any medical term can be easily and understandably broken down when looking at the pre and suffix. Many are aware of the suffix area in terms of diarrhea. Knowing that the prefix of to refers to the ears. From there you can easily see why this could be called a runny ear. (1)
Thefreedictionary.com describes it literally as discharge from the ear. (2) In short discharge or fluid coming from the ear can be called otorrhea.
Ear anatomy- It is important to take into consideration the anatomy of the ear when looking into causes, symptoms, and treatments of otorrhea.
Eustachian tube
- Pressurizes the inner ear
- Located between the middle ear and the back of the throat.
- This is where you feel the “pop” when your ears pop
- Blockage of this tube will give the person a “full” feeling in their ears.
- Easy access for bacteria and viruses to cause infection (1,11)
Outer ear
- The pinna is made of cartilage and skin
- Funnels sound into the ear
Middle ear
- Consists of the ear drum and many tiny bones
- Vibration in the middle ear caused by sound helps to transfer the sound to our nerves
Inner ear
- Consists of the spiral-shaped cochlea and the semicircular canals (labyrinth)
- connects the middle ear to the nerves (12)
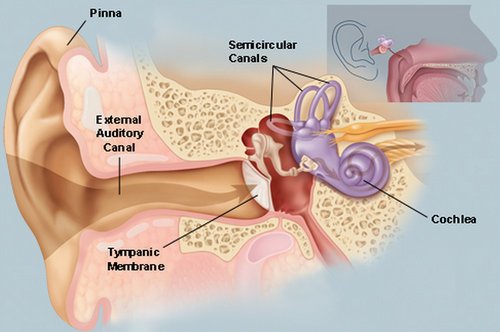
Image 1 : The details of the outer, middle and inner ear.
Picture Source : img.webmd.com
Symptoms of Otorrhea
- Any drainage from the ear
- Regardless of consistency or color
- Could last up to six weeks
- But should be treated immediately.
- Severe edema in the inner and or outer ear
- Any swelling or inflammation (3)
- Slight or partial hearing loss
- Pressure like feeling in or around the ear
- Dizziness or being unsteady
- Stuffy feeling in here
- Pain in one or both ears
- Bloody nose (7)
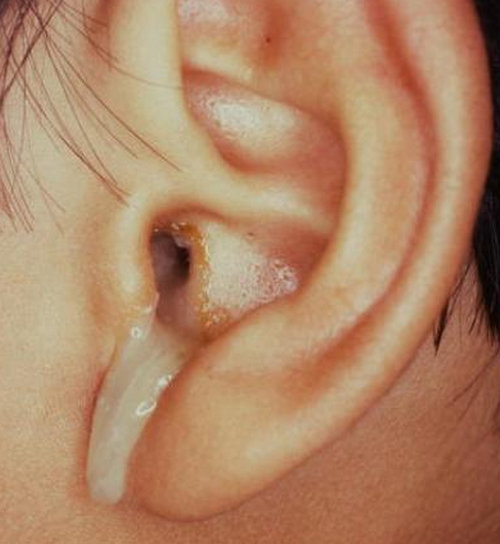
Figure 2 : A purulent think drainage.
Photo Source : pedclerk.bsd.uchicago.edu
Causes of Otorrhea
Otorrhea could have multiple causes each of which with its appropriate causes. This list is not comprehensive please seek medical attention if you note otorrhea:
- Usually otitis media or ear infection
- Bacterial or viral
- Head trauma
- Various causes
- Intracranial complications such as
- Meningitis
- Epidural abscess
- Brain abscess
- Lateral sinus thrombosis
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Subdural empyema
- Carotid artery thrombosis
- External ear canal trauma or disease
- Middle ear disease
- Tympanic membrane rupture or perforation
- Skull injury
- Boil or dermatitis of the canal
- Chronic drainage
- Excessive swimming
- Head colds
- Dermatitis in the ear canal
- Tube placement
- The most common cause for otorrhea in children
- Only placed when a child has shown multiple ear infections.
- Placed to prevent infections but could cause damage to the middle ear
- Even when it causes infection it should help in the drainage process.
- Allows easier access to medication to the inner ear
- Parents should be aware of the possible complications and benefits
- In the case of otorrhea, swelling or redness the parents should seek immediate medical attention(1, 3,6,7)
How can you Treat Otorrhea?
This depends largely on the diagnosis decided upon by your doctor. So the very first treatment must include a trip to see your doctor. Once he has decided the cause of the otorrhea he may do one of the following:
- Spinal fluid.
- If due to an object in the ear simple as removing foreign objects from the ear.
- If the infection is noted then antibiotics will be prescribed.
- In most cases, a lavage or thorough cleaning of the ear canal will be done
- Should only be done by or under the direction of medical personnel.
- To help with inflammation steroid ear drops may be applied
- In the case of a mass, a specimen may be taken. (1,3)
What should I expect when being checked for Otorrhea?
- Full vital signs check.
- A thorough inspection of the ear and surrounding tissue.
- The characteristics of the discharge coming from the ear
- If clear could be central spinal fluid-
- This could be life threatening
- Will appear with a halo on tissue paper
- Indicates perforation of the ear drum
- Is rare and usually only seen after spinal or neurological surgery
- Can be easily documented with MRI screening (4,5)
- If blood could prove trauma
- If purulent or white and thick could show infections
- If waxy this could be completely normal.
- Inner ear inspection using and otoscope
- Possible cleaning of the ear and the surrounding area
- Testing of cranial nerve reactions. (1)
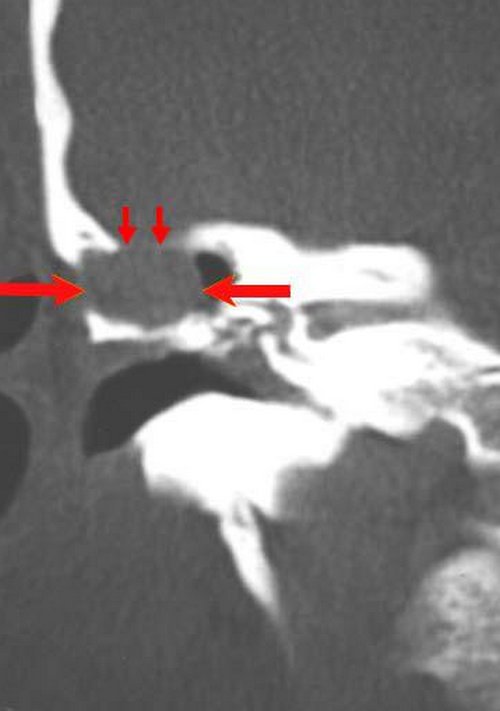
Photo 3 : The results of CT scan.
Picture Source : img.medscapestatic.com
When should I seek medical attention for Otorrhea?
- Any time discharge is noticed coming from the ear
- Noted cranial nerve damage (loss of any of the senses)
- Recent major head trauma
- Fever
- Red and swollen ear (1)
References:
- https://pedclerk.bsd.uchicago.edu/page/otorrhea
- http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/otorrhea
- http://www.aafp.org/afp/2001/0401/p1426.html
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/883160-overview
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/338989-overview
- http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/867955
- http://www.emedicinehealth.com/ear_tubes/article_em.htm
- http://byebyedoctor.com/otorrhea/
- http://www.aafp.org/afp/2001/0401/p1426.html
- http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1301630
- https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/otitis-media.html?ref=search
- http://www.webmd.com/brain/picture-of-the-ear#1