Leishmaniasis
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is Leishmaniasis?
This is a medical disease that is caused by being bit by a female sand fly. There are two different forms of leishmaniasis, which include:
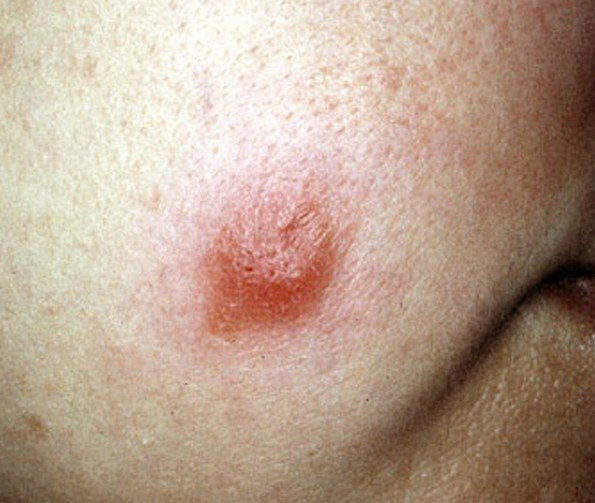
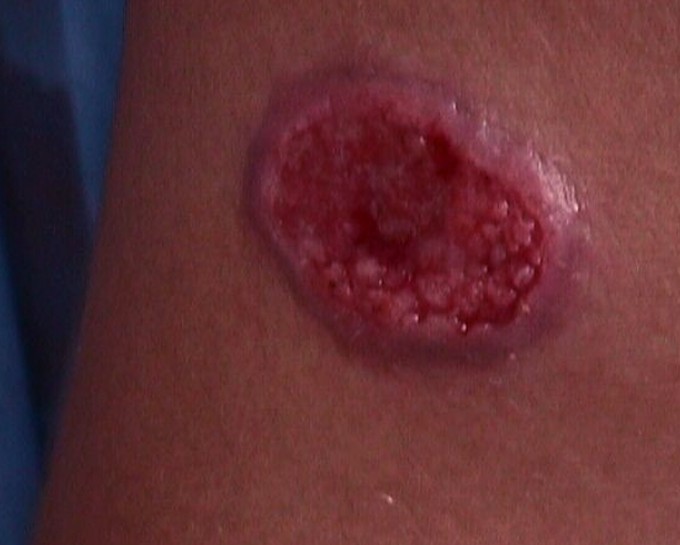
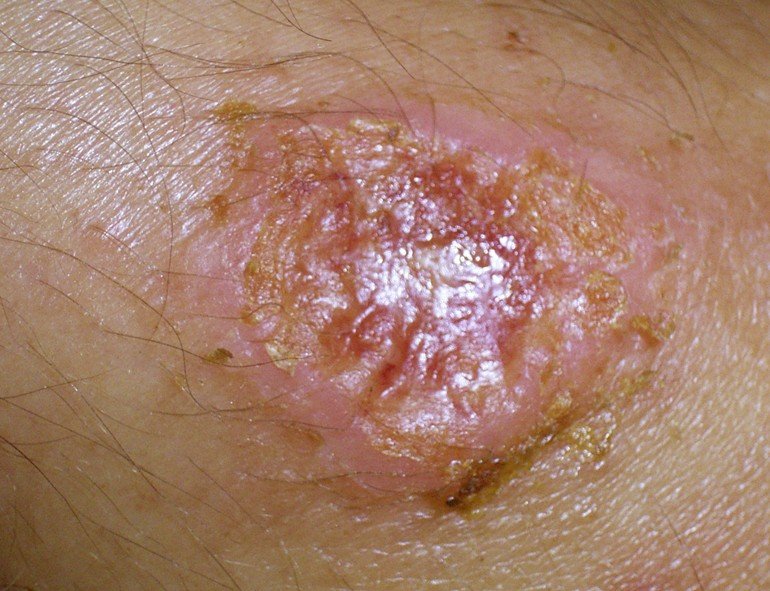
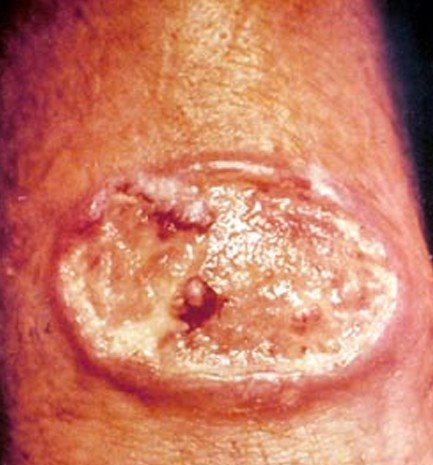
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
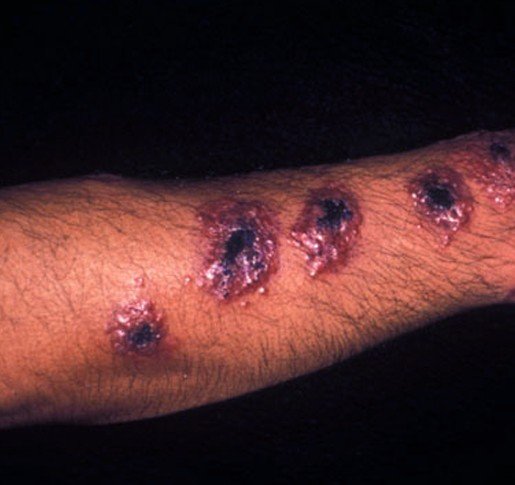
With this form it affects just the mucus membranes and skin. It is the most common form of this disease. You will see skin sores develop at the site where a person was bit by the sandfly and in some they may develop sores on the mucous membranes. Worldwide, each year there are approximately one point five million new cases.
Visceral or systemic leishmaniasis
With this form it will affect your entire body and usually will not occur until two to eight months after you have been bitten by a sandfly. Usually most people will not remember having a skin sore and with this form it can lead to complications that are deadly. Your immune system is damaged by the parasites resulting in a decrease of the numbers of cells that are used to fight diseases. Each year, worldwide, there are approximately point five million new cases.
There have been reported cases of leishmaniasis on every continent except Antarctica and Australia. There have also been reports of cases of leishmaniasis in military personnel that are returning home from the Persian Gulf. You will usually find the sandfly that causes this disease in temperate and tropical countries. In the United States most cases of leishmaniasis are imported from other countries by immigrants or travelers.
Leishmaniasis Symptoms
The symptoms that a person may have depend on the type of leishmaniasis they have.
Cutaneous leishmaniasis symptoms can include:
- Having difficulty breathing
- Skin sores that could become a skin ulcer which will heal very slow
- The skin sore or lesion may appear to resemble psoriasis, acne, or warts
- Having nosebleeds, runny nose, and stuffy nose
- Having difficulty swallowing
- Ulcers and erosion in the mouth, on the gums, lips, tongue, inner nose, and outer nose
Systemic visceral leishmaniasis symptoms can include:
In children these symptoms will usually begin suddenly.
- Diarrhea
- Cough
- Vomiting
- Fever
In adults, they can have a fever from fourteen days to two months along with other symptoms that can include:
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Weakness which will usually increase as the disease becomes worse.
Other symptoms of systemic visceral leishmaniasis may include:
- Discomfort in their abdomen.
- A fever that can come and go in cycles and can last for weeks.
- Having night sweats
- Having skin that is ashen, dark, scaly, and grey.
- Hair that is thinning.
- Loss of weight that can be severe.
- Blood counts that are low.
- Liver and spleen can be enlarged.
- Having a high level of immune globulin in your blood.
In some people with systemic visceral leishmaniasis they are asymptomatic, which means they do not have any symptoms, and do not know they are carrying the parasite.
Life Cycle
There are ten stages in the life cycle of this disease. The first five stages are the human stage and the last five are the sandfly stages.
- Stage 1 – the sand fly will inject promastigotes into a person’s skin during a blood meal, which is the infective stage.
- Stage2 – neutrophils are recruited rapidly to the site of the bite in order to phagocytize the promastigotes.
- Stage 3 – the macrophages consume the parasites that are released by the infected neutrophils.
- Stage 4 – this is the one of the diagnostic stages in which the promastigotes inside the macrophages transform into amastigotes.
- Stage 5 – this is another diagnostic stage in which the amastigotes multiply in cells in various tissues of your body. This includes the macrophages.
- Stage 6 – this is when the sand fly ingests the infected macrophages when it eats a blood meal.
- Stage 7 – this is when the sand fly has ingested the parasitized cell.
- Stage 8 – the amastigotes will transform in midgut into promastigotes.
- Stage 9 – the promastigotes will divide and then migrate to the foregut and anterior midgut of the sandfly.
- Stage 10 – this is when the sand fly will inject into the skin promastigotes when they bite you and is called the infective stage.
Causes
The cause of this disease is from a bite from the female sand fly. There are approximately twenty-one species of sand flies that affect humans including the L. Mexicana complex and the L. donovani complex. The sand flies become infected with the parasite by feeding on infected animals like rodents or dogs or people that are infected with leishmaniasis.
Diagnosis
There are various tests that can be done to help diagnosis if it is leishmaniasis or some other disease. It may also be diagnosed by the physician doing a physical exam and finding signs of an enlarged liver, lymph nodes and spleen. The physician will also do a medical history to find out if the patient has been in an area that is known to have sand flies that could carry leishmaniasis or may have been bitten by a sand fly.
Some of the tests that a physician may perform include:
- A biopsy and culture of your spleen, lymph nodes, skin, and liver where the tissue is looked at under a microscope in order to detect the parasite.
- A biopsy and culture of the bone marrow.
- An indirect immunofluorescent antibody test.
- A Montenegro skin test
- A Leishmania-specific PCR test.
- Complete blood count
- Serologic testing
- Serum protein, albumin, and immunoglobulin tests.
Treatment
The treatment varies from case to case and is usually individualized according to the country where they got the disease and the species of sand fly. The main medications that are used to treat leishmaniasis are called antimony-containing compounds. Two of these medications are:
- Meglumine antimoniate
- Sodium stibogluconate
Some of the other medications that may be used to treat leishmaniasis can include:
- Amphotericin B given intravenously to treat visceral leishmaniasis. This is the only medication that has been approved in the United States to treat this type of leishmaniasis.
- Keteconazole which is given orally and is used for cases of leishmaniasis that arrive in the United States.
- Milterfosine which is not available in the United States
- Paromomycin which is not available in the United States
- Pentaminde
If the sores caused disfigurement you may need to have plastic surgery. If the patient has viral leishmaniasis that is drug-resistant they may have to have their spleen removed. If a person has cutaneous leishmaniasis it is not always treated, especially if there are few lesions which are small and seem to be healing on their own. These are usually just monitored to make sure that they do not become more serious. It is important that you talk with your physician if you think you have leishmaniasis or know that you have been bitten by sand flies because with the right treatment and medicine the cure rates are high. You want to make sure that you get treated become your immune system becomes damaged.