Detached Retina
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is Detached Retina?
Retinal detachment is a condition when the retina or tissue layer of the eye lugs away from the underlying tissue that which nourished and provides it with oxygen. It is an emergency situation wherein a delay in treatment can lead to oxygen deprivation in the cells of retina subsequently permanent vision damage or blindness.
Retinal detachment occur without ethnic background predilection affecting both male and female while the incidence is more in adults between the ages of 40 to 70 years with the aging process being implicated. Children and young adults however, can also get affected with detached retina which is due more on the activities engaged that ca accidentally traumatize the eye potential for retinal detachment.
Retina is a multi layer tissue found at the back of the eye which is sensitive to light and covers about 65 percent of the interior surface of the eye. Retina act as photo receptor of optic of the eyes in which it focuses on the images captured by the front of the eye while the retina transmits the signals to the brain for interpretation as visual images. The chemical and electrical transmission of the retina prompts impulses of the nerves via the optic nerve fibers to send visual images to the visual core of the brain for interpretation. The retina is spherical in shape with a diameter of approximately 22mm and contains millions of cones and rods. Both the rods and the cones produce excitation in pattern and work together with parts of the brain to make representation of images mirrored in the external environment of the eye or the images captured on the front of the eye.
Detached Retina Symptoms
Retinal detachment is an emergency situation that prompt treatment is necessary to evade oxygen deprivation of the cells in the retina. The necessity to prompt treatment is tantamount to prevention of permanent visual damage and blindness. The incidence of detachment of the retina fortunately does not occur abruptly and without warning signs.
Floaters and flashing of lights or photopsia are the initial manifestation of retinal detachment. The eyes will suddenly see visions of debris, strings, spots and other minute debris that seems to float before the eyes. Floaters seen are the result of small solidification of vitreous gel while flashings are due to vitreous gel hitting the retina when it loosened or pulled the retina. The appearance of floaters and flashings are not associated with detachment resulting from retinal tear.
A vision of shadow or curtain perceive in a portion of visual field occurs while the retinal detachment is progressing. The shadow or curtain vision initially begins in the peripheral side of vision then progresses gradually towards the central vision. This kind of vision is usually associated with a retinal tear progressing to detachment of the retina and should be a warning sign to seek immediate medical attention.
Causes
The separation of retina from its underlying tissue can be implicated to numerous factors with retinal tear as the common cause in most cases of detached retina.
Detachment of retina is classified into three basic types according to the mechanism and cause of detachment.
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is the most common type of retinal detachment and occurs as a result of hole, tear or dialyses in the neuronal layer. The mechanism of separation of retina is the result of leakage of fluid seeping into the retinal cavity resulting to separation of retinal pigment epithelium. The hole and tear in the can be associated with age advancement and other disorders and condition that causes the retina to thin. Enough force applied on the thinning retina can create hole subsequently a collapse in the vitreous then detachment of the retina.
Exudative or secondary retinal detachment is the result of fluid accumulation underneath the retina as a result of injury, inflammation and vascular abnormalities. This type of retinal detachment is rare and may also be caused by a tumor growth in the choroid of the retina.
Tractional retinal detachment occurs when the retinal sensory is pulled from the retinal pigment epithelium as a result of fibrous tissue development due to injury and inflammation. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy is the common cause of this type of retinal detachment including penetrating trauma.
Other factors are also being considered to contribute for predisposition of retinal detachment and these include the following:
- Blunt blow to the orbital
- Head concussion
- Penetrating trauma
- Diseases and disorders of the eye previously experienced such as Lattice degeneration, myopia, uveitis
- Certain eye drops used to treat previous eye condition
- Complication from cataract removal or surgery
- History of retinal detachment in the family
- Extreme activities and high-impact sports which can cause eye trauma
- Rapid change in acceleration and deceleration causing increase pressure in the eye
Treatment
Early treatment of retinal detachment is necessary before it reaches the central area or the macula of the eye. Prompt treatment can evade the potential for permanent damage in the eye which can lead to blindness. The goal of treating and reattaching detached retina is to improve the visual while preventing irreversible damage to the eye. Identification of retinal hole or tear in early diagnosis is vital in preventing the hole from progressing to detachment. Retinal hole or tear can be treated with photocoagulation directed at the retinal tear to weld or burn the tear around the retina. Cryopexy is another procedure intended to seal the tear around the retina.
The detached retina on the other hand is basically reattached with surgical procedures such as:
Pneumatic retinopexy through placing bubbles or gas in the vitreous to seal the detached retina
Scleral buckling is a procedure of suturing the sclera and the affected area using a silicone rubber or sponge to indent the surface of the eye and relieve vitreous tugging of the retina
Recovery Time
Surgical procedures for repairing retinal detachment can have the patient stay for overnight in the hospital or can be treated as outpatient. The recovery for clear vision however, may last for several months which may need regular monitoring and prescription eyeglasses. Surgical procedures have high rate of recovery although there are cases where visual ability of the patient is lost.
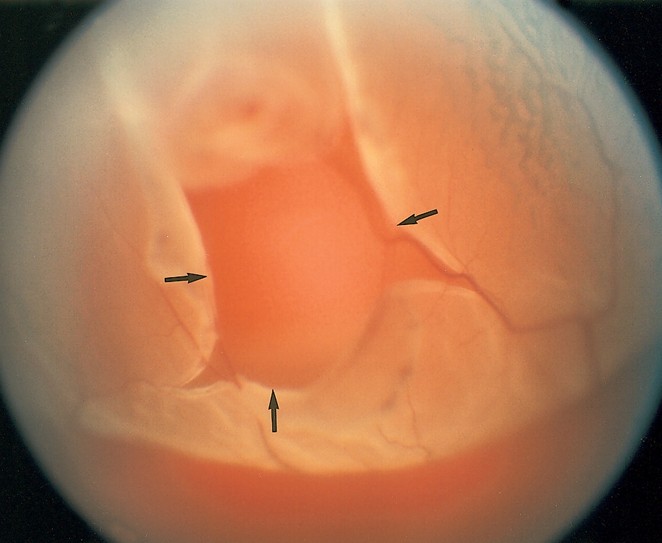
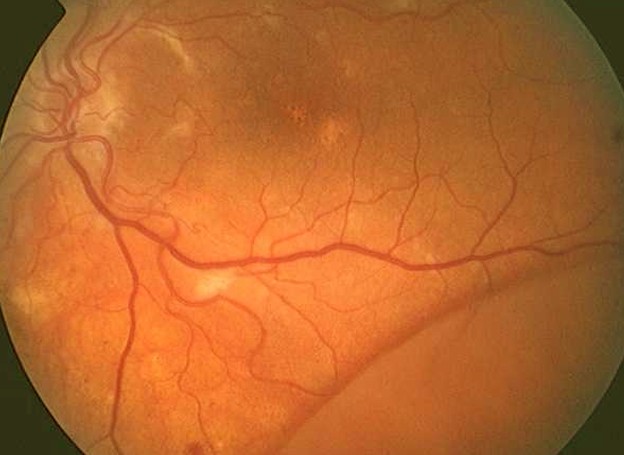
Detached Retina Pictures
Collection of images, photos and pictures of detached retina…