Exostosis
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
Exostosis Definition
What is exostosis? It is an overgrowth of bones that can take place in any part of the body. It is a non-cancerous condition.
Basically, it is just a bone that grows on the surface of another bone. It is also known as osteoma. The growth is prominent in the ears, knees, shoulders, ankles, jaw, and elbows.
What are the clinical manifestations?
The symptoms of exostosis vary depending on the root cause. Usually, the patient will complain of mild to moderate pain. The severity of pain depends on the location, shape, and size of exostosis.
If the cause is surfer’s ear, the patient will complain of pain and difficulty in hearing. If the patient complains of extreme pain, then it could probably be due to subungual exostosis. A buccal exostosis is the painless type. (1, 2, 3)
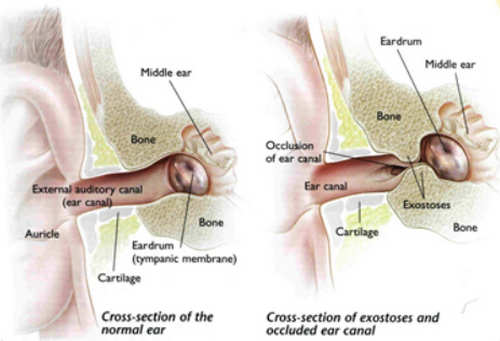
Image 1: An image comparison between a normal ear and an ear with exostosis and occluded ear canal.
Picture Source: www.earspecialistperth.com
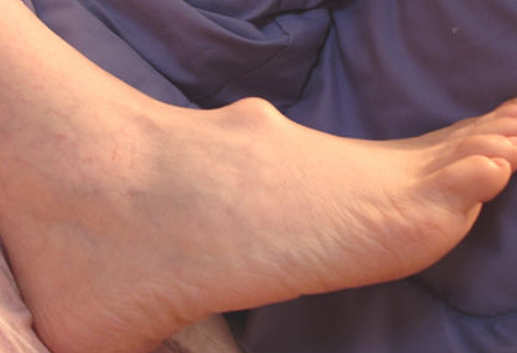
Photo 2: An example of foot exostosis or saddle bone deformity.
www.just-health.net
Possible causes of exostosis
- Environmental stress – A perfect example is when the bone grows into the ear canal.
- Excess build-up of calcium – An excess calcium in the body can sometimes lead to new bone growth.
- Damage to the joints – A damaged joint can cause strain, which could result to the development of small bone deposit on the joint or in its surrounding areas.
- Unknown reason – Sometimes, there is no exact reason why exostosis exist. (1, 4, 5)
Exostosis Types
- Subungual – It affects the fingers and toes. It usually grows under the nail, especially the big toe. The cause of subungual exostosis is not clear, but it is linked with trauma to the toe. It is more common in women and can occur at any age. (9)
- Buccal – It affects the jawbone. The lower jaw is more prominent than the upper jaw. It is the less common type of exostosis.
- Retrocalcaneal – It affects the heel bone,e specially the Achilles tendon. It is common in adults, especially women. Reasons for retrocalcaneal exostosis include wearing tight fitting shoes that irritate the bones, short or tight Achilles tendon, bursitis, inflammation, and inflamed pad.
- Dorsal – This is an exostosis foot or also referred as dorsal mid-foot exostosis. People with dorsal exostosis have a hard time wearing shoes, especially if they were enclosed shoes.
- Metatarsal cuneiform – It is a type of exostosis that forms on the top of the foot just above the arch. It is also called saddle bone deformity. It is common in both men and women and affecting the age group of 25 to 60. (7, 10)
- Osteocartilaginous – It pertains to the growth of both cartilage and bones. The other term is exostosis osteochondroma. It affects the ends of the long bones.
- Hereditary multiple exostosis (HME) – It is an inherited form of exostosis wherein the bony growth randomly occurs in the body. The likelihood to experience HME is one in fifty thousand people. (10)
What are the possible complications?
- Exostosis disturbs the normal progression of the bones leading to unequal lib growth.
- Moving can be painful due to join impingement.
- You can be suffering from pain even if you are at rest.
- Disturbed bone growth can lead to bow legs or bowed ankles.
- There is an increased risk for malignancy, especially if the bone growth affects the pelvis.
- The patient will complain of pain, swelling, discoloration, and weakness. (5, 6, 7)
How to diagnose ?
The physician will conduct a thorough physical examination to detect any unusual bony growth. The doctor will also conduct a complete family history and will take an x-ray of the affected part of the body.
Exostosis Treatment
To come up with the best possible treatment, the doctor will determine the extent of the problem. In some instances, the bone growth is allowed to remain to its place, especially if it is painless and not always expose.
If you find it aesthetically displeasing, then your best option is to have it removed. Exostosis removal is a type of surgery. Most of the time, it is an invasive type. There could be possible complications, especially if the bony growth is situated in delicate parts of the body. (4, 7, 8)
If the bony growth is painless and not cancerous, it is usually left in place. If the exostosis affects the ears, the bone growth is remove to relieve tension and improve hearing. On the other hand, if you are suffering from subungual exostosis, the best treatment approach is surgical excision.
If the exostosis causes severe pain and discomfort, the doctor will prescribe steroids or oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Heel lifts can also help improve the condition of the patient. A heel lift is a wedge placed under the heel to lift it. The purpose of this tool is to decrease the tension of the Achilles tendons.
If the patient complains of severe pain, the doctor will decide to immobilize the affected foot so that the strain and stress will be reduced significantly. When deemed necessary, the doctor will cast the affected foot and let you use the crutches so as not to put any tension on the affected foot. To speed up the healing process, the patient is strongly advised to undergo a physical therapy. If these conservative treatment approach fail to work, the best option is for the patient to undergo surgery.
Lifestyle modification plays a very important role in the overall well-being of the patient. The primary goal is to improve the quality of life, prevent any irritation or tension on the affected part of the body, and to live life normally. If exostosis affects your foot, then you should carefully choose your footwear. As much as possible, you have to avoid wearing heels and other tight fitting shoes.
If you want the bony growth to be removed, make sure that your doctor explains to you the pros and cons of the procedure. It is important to come up with an informed choice. Consult your doctor and ask the best treatment and management approach for your exostosis. (3, 5, 8)
References:
- https://radiopaedia.org
- https://en.wikipedia.org
- mddk.com
- www.aboutkidshealth.ca
- www.dermnetnz.org
- www.orthobullets.com
- www.pathologyoutlines.com
- www.everydayhearing.com
- www.docpods.com
- Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors: Clinical Features, Imaging, Pathology and Treatment By Mario Campanacci