Leukopenia
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is Leukopenia?
Leukopenia definition
White blood cells are the army of the body. They are medically called leukocytes. There are 7000 white blood cells/microliter of blood. If the number of white blood cells goes below the normal level, the condition is called leukopenia.
It compromises your health because the immune system is severely weakened. (1, 2)
Leukopenia ICD-10-CM code – D72.819
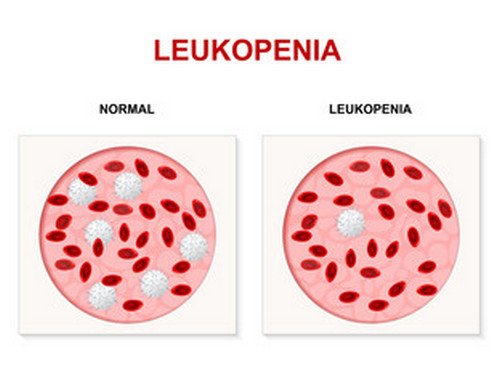
Image 1: A comparison image between a normal white blood cell and low white blood cell (leukopenia)
Photo Source: www.istockphoto.com
Picture 2: A microscopic image of leukopenia.
Image Source: classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com
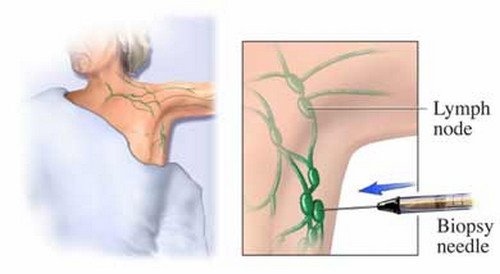
Photo 3: Lymph node biopsy, one of the diagnostic procedures for leukopenia.
Picture Source: images.lifescript.com
Leukopenia symptoms
What are the signs and symptoms of leukopenia? The patient usually does not notice the signs of leukopenia.
Clinical manifestations are only evident if the white blood cell count is extremely low. Signs and symptoms include the following:
- Fever (38 degrees and up)
- Chills and sweating at night
- Unexplained weight loss
- Weakness
- Body malaise
- Dizziness
- Frequent headache
- Menorrhagia (in women with severe leukopenia)
- Metrorrhagia (bleeding in the uterus not related to menstruation) (2, 3, 5)
Leukopenia causes
There are a number of health conditions that cause leukopenia. These include the following:
- Suppression or damage to the bone marrow – Damage to the bone marrow can be caused by certain chemicals and/or toxins. It can also be caused by radiation therapy and side effects of certain drugs.
- Bone marrow disease – Diseases of the bone marrow can significantly affect the production of white blood cells. It might not produce the regular number of white blood cells or it produces an excess amount of a certain type of white blood cell.
- Cancer that metastasize to the bone marrow – Any types of cancer that metastasize to the bone marrow could lead to leukopenia.
- Sepsis – It can reduce the number of white blood cells in the body.
- Autoimmune disease – It is when the immune system attacks healthy cells. The immune system thinks that the white blood cells are a foreign substance and so they attack it.
- Hypersplenism – The spleen is enlarged, which destroys the blood cells. If left unmanaged could lead to anemia and leukopenia.
- Side effects of medications – Some drugs can affect the level of white blood cells such as clozapine, lamotrigine, and sodium valproate, to name a few.
- Other health conditions – What is a condition that can cause leukopenia? Some medical conditions can affect the level of white blood cells in the body such as thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, aplastic anemia, vitamins and mineral deficiency, tuberculosis, and parasitic infections.
- Other factors – Other possible causes of leukopenia are nutrient deficiency, stress, and malnutrition. (4, 5, 7, 8, 9)
Classifications
- Granulocytes/polymorphonuclear leukocytes – They have granules (membrane-bound enzymes). Granulocytes have three types: neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils.
- Agranulocytes/mononuclear leukocytes – They do not have granules in their cytoplasm. Agranulocytes WBCs are monocytes, lymphocytes, and macrophages.
There are various forms of leukopenia but the most common form is neutropenia. Neutrophils consist about ¾ of the total white blood cell count. Neutrophils are the primary fighters of the immune system. They get rid of all types of infections (bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasites). (6, 9, 10)
Diagnosis
The doctor will order for CBC (complete blood count) to check the components of the blood and confirm the diagnosis of leukopenia and neutropenia. If the neutrophil count is less than 500 per microliter of blood, then it confirms the diagnosis of neutropenia in adults. Other tests include complete haemogram, which counts the white blood cell of each type.
Aspiration of the bone marrow can also be done if the analysis result is not clear. A lymph node biopsy can also be ordered wherein a part of the lymph node tissue is removed and examined and analyzed under the microscope. (1, 3, 5)
Leukopenia treatment
The treatment of leukopenia primarily depends on the one that causing it. For an instance, if it is a side effect of a medication, then the doctor might decide to stop the medication and switch to something less risky to the patient.
If the leukopenia is caused by a genetic condition, then the patient should be put on a granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. A bone marrow derived growth factor can also enhance the production of white blood cells.
Other leukopenia medications include antibiotics and antifungals to treat bacterial and fungal infections. (2, 6, 7, 9)
Natural treatment remedies
Diet plays a very important role in improving the overall condition of the patient. The patient should have an immunocompromised diet. It is also called neutropenic diet or low bacterial diet. The patient is put on such diet to reduce the possibility of contacting harmful microorganisms from the food. Fresh fruits and vegetables should be completely avoided.
The meat should be thoroughly cooked through. Avoid eating raw or rare cooked meat. Do not eat yogurts as they contain live bacteria. (1, 3)
You should rest. Conserve your energy. Stay away from physical activities, especially the strenuous ones. Avoid physical contact. Be mindful with your surroundings. As much as possible, you should avoid even the littlest scrapes or cuts because even the minor cuts can be a start of infection. If you want to shave, make sure you are going to use an electric razor.
As much as possible, you shouldn’t brush your teeth or use mouth care products that contain strong ingredients. If you want to brush your teeth, you should use gentle bristles. (3)
Since you are prone to infection, you should make it a habit to wash your hands. Avoid sick people. Stay away from a huge crowd. Do not stay in a place that can put you at risk for infection such as fish bowl, animal cages, and dirty stuff.
If you are prone to leukopenia, the doctor will regularly check the level of white blood cells to lower the chance of complications. (8, 9, 10)
What are the possible complications of leukopenia?
- There might be a need to delay the treatment of the patient with cancer.
- Severe leukopenia can increase the possibility of septicemia, which is a life-threatening condition.
- If not managed well, the patient could die of leukopenia.
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leukopenia
- https://www.healthline.com/health/leukopenia
- https://www.news-medical.net/health/Leukopenia-Causes.aspx
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/low-white-blood-cell-count/basics/definition/sym-20050615
- http://www.cancertherapyadvisor.com/hematology/leukopenia/article/596822/
- http://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/leukopenia
- http://healthooze.com/leukopenia/
- https://emedicalhub.com/leukopenia-definition-causes-symptoms-treatment-workup/
- http://www.antimicrobe.org/e19.asp
- http://leucopenia.org