Histoplasmosis
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is Histoplasmosis?
This is a medical condition that affects your lungs and can affect other parts of your body. If it affects other parts of your body it is referred to as disseminated Histoplasmosis. Histoplasmosis is spread through airborne spore so people like construction workers, farmers, and landscaper workers may be prone to suffer from this medical condition. It can be a serious medical condition especially for people with immune systems that are compromised and infants. It can be found world-wide but in the United States it is usually found in the Ohio and Mississippi river valleys. In the United States there are reported approximately two hundred fifty thousand cases each year. The disease has also been called bird-fancier’s disease and Ohio River Valley fever. Most of the cases are found in equatorial Africa or in river valleys.
Symptoms
There are several varieties of histoplasmosis and some of the mildest type produces no symptoms but in some cases it can cause severe infections and be life-threatening. They symptoms are similar to pneumonia. Approximately ninety percent of the cases produce no symptoms. Normally the symptoms of this medical condition will appear three to seventeen days after a person has been exposed and can include:
- Chills
- Fever
- Muscle aches
- Non-productive or dry cough
- Headaches
- Discomfort in your chest
- Sweats
- Abdominal pain three to fourteen days after being exposed
- Fatigue
Histoplasmosis can also cause a rash and joint pain in some people. If a person has an underlying lung condition like emphysema they could get a chronic form of this disease that can cause additional symptoms such as a cough in which the person coughs up blood and loss of weight.
If the disease spreads out of your lungs to other parts of your body by may have symptoms that could include:
- Pneumonia
- Pericarditis
- Anemia
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Ulcers in your intestinal tract, tongue, or mouth
- Meningitis
Causes
The cause is from reproductive spores (cells) of fungus called Histoplasma capsulatum that is often found in bat and bird droppings or from soil that is contaminated with either of these droppings and has been disturbed. It is usually transmitted when the spores get into the air because they are very light and float on the air, such as during demolition projects or during cleanup of bird or bat droppings and people breathe in the contaminated spores. It is commonly found in pigeon or chicken coops, caves, parks, and old barns. Even if you have had this medical condition you can still get it again but the subsequent infections are milder. It is not a contagious disease so it does not spread from animal to person or person to person.
This was first described in 1905 y Samuel Darling by was not diagnosed until 1932 by Edna Tompkins and Katharine Dodd when they were treating an infant with this medical condition. It has been found world-wide since the 1930’s.
Diagnosis
Physicians may sometimes have trouble diagnosing histoplasmosis because the patient may not give the physician a history of possible exposure to areas that may be contaminated with the fungus spores. Treatment that is done depends on the area of your body that is affected. For mild cases of this medical condition it is not necessary to do any testing but in order to choose the appropriate treatment where the disease may be life-threatening it is crucial to do testing. Your physician may only test for histoplasmosis if you work in area that is high risk for developing this medical condition or if you have a severe infection. Your physician may suggest that a combination approach be used to find evidence of the disease by doing a fungal culture by taking samples of:
- Urine or blood doing a complete blood count because a low white blood count may occur in someone who has chronic progressive histoplasmosis. The physician is also checking for proteins or antibodies that could indicate contact with these fungus spores.
- Secretions from your lungs
- Doing a biopsy on lung tissue
- Bone marrow
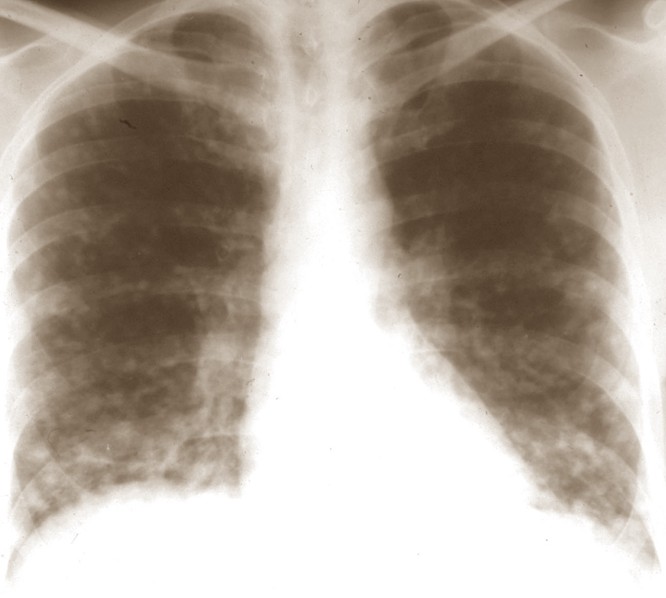
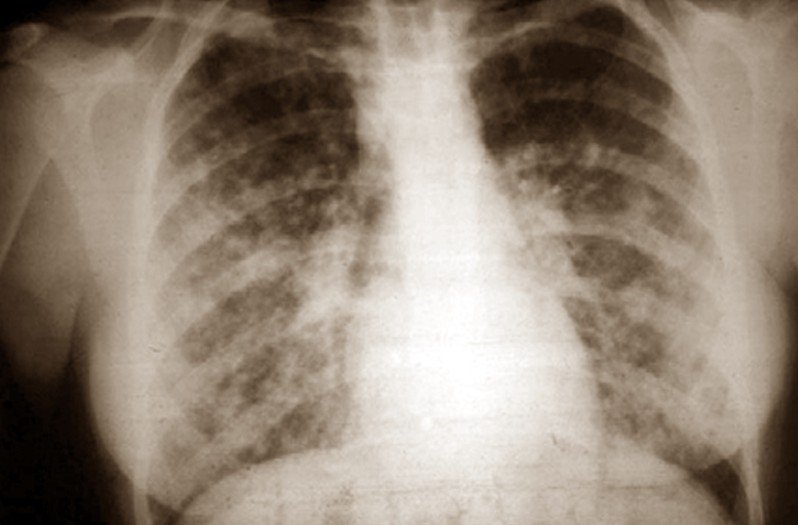
It can take as long as six weeks to get the results from urine or blood tests or the sputum cultures. The physician may also order a chest x-ray to see if there are any changes in your lungs such as lymph nodes that are enlarged or have any cavitations which can occur in acute and chronic progressive disseminated histoplasmosis.
Treatment
If the symptoms are not severe the physician may opt to do no treatment or have you take over-the counter medications and rest. If you have the symptoms and are severe the physician can treat it with antifungal medication, which could be one or a combination of two or more. When you have trouble breathing or your lungs have been infected for more than thirty days the physician may give you oral antifungal medications. These may require treatment by using an IV. Severe infections may require the medication intravenously, which is how they give the strongest medication. There are some types of antifungal medications in a pill form. In some cases a person has to take the medication for up to twenty-four months. One type of antifungal medications that is commonly prescribed is Itraconazole. If you have had a case of histoplasmosis before and get it again you have partial protection from getting a severe form of the disease the second time.
For the people who have no symptoms or mild symptoms the infection will usually go away within three weeks without treatment.
Histoplasmosis Pictures
Photos, Images and Pictures collection of Histoplasmosis…