Iridocyclitis
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
The eyes are the windows to the soul. They are a sensitive organ. If not taken care of, eye infection and other eye-related diseases could possibly happen.
As we all know, the eyes are extremely sensitive organs. The iris, the colored part of the eye is prone to infection.
What is iridocyclitis ?
If it gets inflamed, the condition is called iritis. The eyes also contain ciliary body, the muscles, and tissues responsible for eye focus. If both the iris and ciliary body are inflamed and infected, the condition is called iridocyclitis. (1, 2, 3)
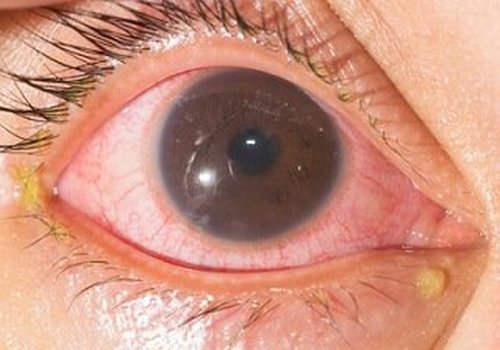
Photo 1: A patient with clinical manifestations of iridocyclitis.
Picture Source: www.hxbenefit.com
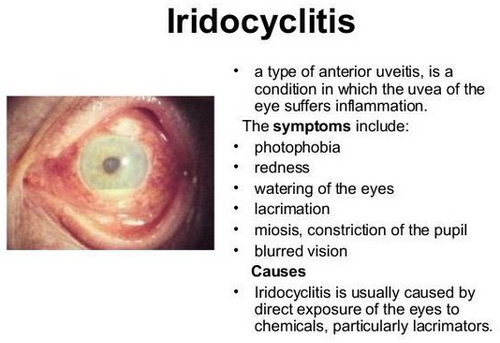
Image 2: The classic symptoms of iridocyclitis.
Photo Source: pbs.twimg.com
Iridocyclitis symptoms
- Redness of the eyes
- Soreness and pain (2)
- Sensitivity to light/fear of light (photophobia)
- Problem in vision
- Watery eyes (3)
- Painless blurring of vision (Chronic iridocyclitis)
- Presence of floaters (chronic iridocyclitis)
- Severe loss of vision (chronic iridocyclitis)
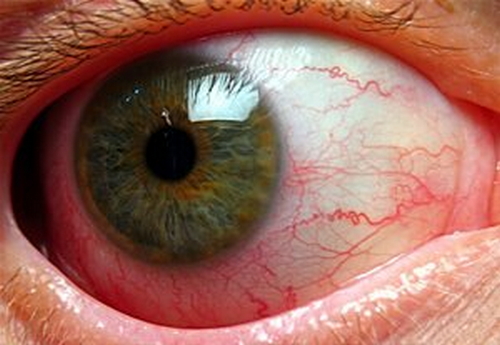
Picture 3: A close up view of the patient’s eye infected with iridocyclitis.
Image Source: www.hxbenefit.com
What is the cause of iridocyclitis?
- Exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Viral infection affecting the eyes such as herpes zoster virus, gonorrhea, and HIV.
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, which causes a part of the eyes to swell.
- Autoimmune disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, Ankylosing spondylitis, and Reiter’s syndrome.
- Side effects of medical treatment.
- Inflammatory disease such as ulcerative colitis and psoriasis.
- Cancer such as ocular melanoma, lymphoma, and leukemia. (3, 4, 5)
Types of iridocyclitis
- Acute iridocyclitis – The onset is sudden and last for more than a month.
- Chronic iridocyclitis – What does chronic Iridocyclitis mean? It means that the condition exists for more than a month. It is asymptomatic and linked with other disease conditions such as syphilis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Endogenous Iridocyclitis – It is caused by internal microbes.
- Exogenous Iridocyclitis – It is linked with uveal injury secondary to external microbes.
- Granulomatous Iridocyclitis – It is caused by keratic deposits.
- Non-granulomatous Iridocyclitis – It is linked with small cellular deposits. (4, 5, 6)
Fuchs heterochromic iridocyclitis is a chronic U/L – unilateral uveitis with classical triad :
-
heterochromia,
-
glaucoma and cataract
-
keratitic precipitates on the cornea (posterior) surface.
Iridocyclitis in children
Children with rheumatoid arthritis are prone to iridocyclitis. The frontal section of the uvea is inflamed, which might cause scar in the pupil.
If not treated right away could affect the ability of the pupil to focus. Many people believed that arthritis only affects the joints and tissues. What they didn’t know is that it also affects the eyes. (4, 7, 8)
Prevalence rate
Iridocyclitis usually affects people between 20 years old and 59 years old. It is less common in children. It does affect both genders though regardless of the age. The incidence rate is one in every 4500 population. Iridocyclitis is more prevalent in western countries than in Asian countries. (4, 8)
How to diagnose iridocyclitis?
- Eye examination – The eye doctor will thoroughly examine the eyes of the patients. The doctor will dilate the pupil and check for the presence of abnormalities.
- ANA (Anti-nuclear Antibody) Test – This is the diagnostic procedure used to detect iridocyclitis in patients with asymptomatic iridocyclitis.
- Eye Chart Test – The patient’s vision is checked to detect if there is something that could dramatically affect the patient’s vision.
- Funduscopic Examination – A light is passed through the eyes to see if the pupil dilates. It also helps examine the inside structure of the eyes.
- Ocular Pressure Test – A special instrument like tonopen or tonometer is used to check the pressure inside the eyes.
- Slit Lamp – It is a special type of microscope used to check the parts of the eyes. It will help detect inflammation and any abnormalities.
- X-ray – It detects co-existing arthritis, which is one of the medical conditions linked with iridocyclitis.
- Blood Test – It helps detect the presence of infection and autoimmune disease. (2, 5, 8, 9)
Image 4: An eye drop is one of the common treatment modalities for eye infection like iridocyclitis.
Picture Source: www.rowland98.com
Iridocyclitis treatment
- Steroidal eye drops – It is applied topically to alleviate swelling and inflammation. Examples of steroidal eye drops are prednisolone and dexamethasone.
- Oral steroids – It is used to treat severe cases of iridocyclitis.
- Pain reliever – For effective pain management, the doctor will order drugs containing at least .25% to 1% atropine and scopolamine. Cycloplegic drugs are also helpful in alleviating pain and discomfort. Painkillers like paracetamol.
- Subconjunctival steroid injection – it is the last resort and should only be given if all other methods failed. However, steroids shouldn’t be given to patients with an eye infection or corneal ulcer.
- Patients with photophobia or sensitivity to light are strongly advised to wear dark glasses.
- Immunosuppressive drugs – It is used to control the adverse effect of steroids.
- Treat the underlying condition – If iridocyclitis is caused by an underlying health condition such as in the case of autoimmune disease, the underlying health condition should be treated first. Iridocyclitis will not improve unless the underlying health condition is taken care of.
- TNF alpha blockers – It is used to treat iridocyclitis secondary to Behcet’s disease. Examples of TNF alpha blockers are Infliximab and Etanercept. (1, 4, 6, 8, 9)
Outcome and prognosis
The recovery time and prognosis varies depending on the type of iridocyclitis and the response of the patient to treatment. Mild iridocyclitis usually subsides in just a few weeks. On the other hand, a severe type of iridocyclitis would take a few months to even a year to subside. Without proper treatment, the condition can get worse over time.
There is a possibility that the patient’s eyesight will be completely damaged. There is also a possibility of developing cataract and glaucoma. If treatment is given to the patient in a timely manner, the prognosis is very good.
The patient can fully recover in just a few weeks without complications. Without proper and timely treatment, the prognosis is poor. (2, 3, 5)
What can you do to prevent iridocyclitis?
The eyes are some of the most important parts of the body. It is just right to take good care of them. Make sure you keep your eyes clean at all times. Stay away from things that could jeopardize your eye health. As much as possible, you should avoid eye injuries.
You should increase your immunity so that you will not be susceptible to various forms of diseases. If you feel like there is something unusual with your eyes, you should immediately consult an eye specialist. (2, 4, 6, 7)
References:
- http://www.ilpi.com/msds/ref/iridocyclitis.html
- https://www.hxbenefit.com/iridocyclitis.html
- https://www.aao.org/bcscsnippetdetail.aspx?id=5764897b-854f-4d56-a9a7-580944c1ddb1
- https://www.slideshare.net/islammosman1/iridocyclitis
- https://healthsurgical.com/iridocyclitis.html
- https://www.epainassist.com/eye-pain/chronic-iridocyclitis-or-uveitis
- http://www.ivyroses.com/Define/Iridocyclitis
- https://www.medigoo.com/articles/iridocyclitis/
- http://www.checkorphan.org/diseases/iridocyclitis