Is Bronchitis Contagious ?
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is bronchitis?
It is the swelling or inflammation of the bronchial tubes, a structure in between the mouth, nose, and lungs.
It serves as the passageway for air. Specifically, bronchitis happens when the lining of the bronchial tubes is inflamed. There are two types of bronchitis: acute and chronic.
- Acute bronchitis – What is acute bronchitis? It is a short span bronchitis. It follows a viral infection such as colds and flu. The patient experiences a feeling of chest discomfort, cough with mucus, shortness of breath, and fever. This condition usually lasts a few days, but it could also take weeks for the patients to be completely healed. (1, 2, 3)
- Chronic bronchitis – It is a serious and ongoing illness. The clinical manifestations include a persistent productive cough that has been going on for three months, breathing difficulties and a feeling of discomfort. If the patient’s condition is not managed properly, it could lead to COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). (3, 4)
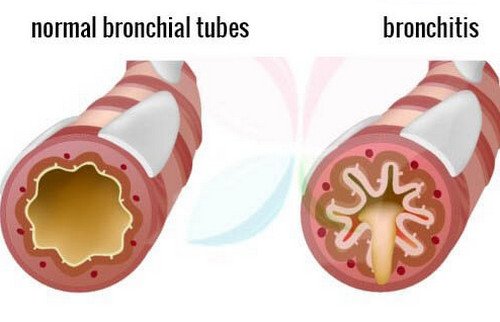
Photo 1: A comparison image between a normal healthy bronchial tubes and an inflamed bronchial tube.
Picture Source: pinnaclemarketinggrp.com
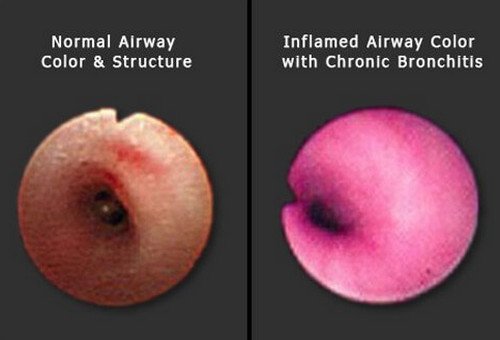
Picture 2: The image on the left depicts a normal airway color and structure. The image on the right in an inflamed airway, which is one of the clinical manifestations of chronic bronchitis.
Photo Source: images.onhealth.com
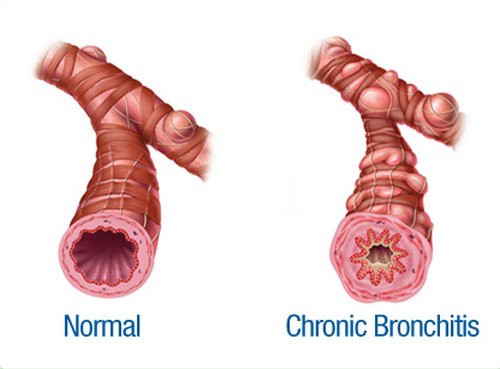
Photo 3: Images of normal airway and airway of patients with chronic bronchitis.
Image Source: www.emedmd.com
What are the causes of bronchitis?
- A virus, especially in the case of acute bronchitis.
- Bacteria (chronic bronchitis)
- Exposure to substances that can irritate the lungs (air pollution, fumes, vapors, dust, and tobacco smoke) (2, 4, 5)
What are the symptoms/clinical manifestations?
- Persistent cough
- Low fever and chills
- Wheezing sound when breathing
- A feeling of tightness in the chest or a feeling that your chest is full or clogged.
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Body ache
- Shortness of breath
- A productive cough (clear, white, yellow, or green sputum)
- Stuffy nose (6)
Who are at risk?
- Those with weak immune system are at risk. Older adults, babies, and young children are at risk because they have a weak immune system.
- Those who are chronic smokers are at risk too.
- Those exposed to second-hand smoke are at risk.
- People who are exposed to harmful chemicals, dust, and fumes.
- Those who live or travel to a place with poor air quality/pollution. (6, 7, 8)
How to diagnose bronchitis?
To accurately diagnose bronchitis, the doctor will conduct a series of tests. He will also take out your past medical and surgical history. The doctor will check for abnormal sounds in the lungs. A significant part of the assessment process is checking the oxygen level in the blood, checking the mucus, conducting pulmonary lung function test, blood test, and chest x-ray. (9, 10)
Is bronchitis contagious?
Can you catch bronchitis from another person? Is it a contagious disease? Is bronchitis contagious after taking antibiotics? Is bronchitis contagious through kissing? Is bronchitis contagious to babies? Chronic bronchitis is not contagious. Acute bronchitis is the contagious type.
It can be spread from person to person through coughing. You can catch the infection if you breathe in the virus or touch things coated with the virus. The mode of transmission is droplets. If the person with acute bronchitis sneezes, talks, or coughs and the droplets get into your mouth or nose, then most likely you will be infected.
It can be spread through kissing an infected person. It is also contagious to babies considering that babies and small children have a weak immune system. (1, 2, 4, 5)
Is bronchitis contagious after taking antibiotics?
Antibiotics for bronchitis should be taken for seven consecutive days. If the symptoms start to disappear, the mucus will turn from greenish to yellowish to white. If the mucus is already white, it is an indicator that the patient is no longer contagious. (2, 6, 7)
How is bronchitis treated?
If you are suffering from bronchitis, it is important for you to take a rest and drink more fluids. To ease your breathing, you need to use over the counter cough suppressants. Acute bronchitis usually goes away without needing specific treatment. The doctor will sometimes prescribe medications to improve the symptoms.
The doctor will order for cough medicine to bring up the mucus and remove anything that could irritate the lungs. The patient should also take mucolytics to loosen the mucus and facilitate coughing up sputum.
Bronchodilators are also prescribed to keep the bronchial tubes opened and facilitate easy removal of the mucus. In some instances, the doctor will prescribe glucocorticoid steroids and anti-inflammatory medications so as to decrease chronic inflammation and prevent tissue damage.
For patients with breathing difficulty, an oxygen therapy is needed. The patient might also need to work with a respiratory therapist. For infection caused by bacteria, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection and prevent secondary infection. (5, 8, 9)
What are the possible complications?
Pneumonia is one of the common complications of bronchitis. Pneumonia takes place when the infection reaches the lungs causing the air sacs to be filled with fluid. It is more likely to occur in older adults, people with a weak immune system, chronic smokers, and people with an organ-related disease. (1, 2, 10)
Is bronchitis deadly?
Chronic bronchitis is life-threatening. It could lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other types of severe lung disease. It could eventually affect other organs of the body including the heart. Shortness of breath and heart complications make bronchitis a deadly disease. (2, 3)
When should you contact your doctor?
You should immediately contact your doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Coughing out of blood.
- A cough has been going on for three weeks.
- The chest pain is intense.
- You couldn’t sleep soundly at night.
- You notice a foul-tasting fluid in your mouth.
- You have a high fever.
- You have an unexplained weight loss.
- You are short of breath and your breathing produces a wheezing sound. (4, 5)
How can you prevent bronchitis?
- The best way to prevent bronchitis is to stop smoking tobacco completely. For a non-smoker, you should limit your exposure to second-hand smoke.
- Limit if not completely avoid your exposure to substances that can irritate the lungs such as smoke, vapors, dust, fumes, and air pollution. When being exposed in an environment with lung irritants, you need to wear a mask to cover your mouth and nose.
- Make it a habit to wash your hands to prevent the spread of harmful microorganisms.
- Get pneumonia and flu vaccine.
- Keep your pertussis vaccine up to date.
- Keep your body healthy so that you will have a shield against infection. Eat a healthy balanced meal. Take multivitamins, especially if you don’t like eating fruits and vegetables.
- Keep your body clean at all times. Cleanliness and hygiene are a must.
- Live a healthy lifestyle. Stay away from vices including smoking, alcohol, and drug abuse.
- Stay away from people with an infectious disease. (1, 5, 6, 9)
References:
- https://www.buzzle.com/articles/how-serious-is-bronchitis.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bronchitis
- https://www.webmd.com/lung/understanding-bronchitis-basics
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bronchitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20355566
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/8888.php
- https://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Bronchitis/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- https://www.medicinenet.com/bronchitis_acute/article.htm
- https://www.medicinenet.com/chronic_bronchitis/article.htm
- https://www.emedicinehealth.com/bronchitis/article_em.htm
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/bronchitis