Sarcopenia
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is a Sarcopenia?
It is a degenerative disease characterized by loss of muscle mass, strength, and function. The International Osteoporosis Foundation said that muscle mass starts to depreciate by the time a person reaches 40 years old.
By the time the person reaches 60 years old loss of muscle tissues becomes rapid. (1, 2)
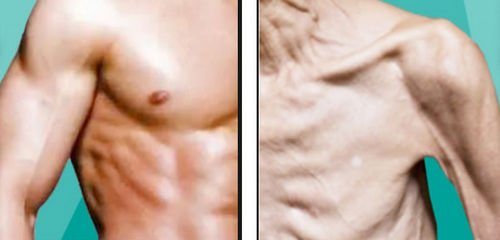
Image 1: Differentiating muscle mass of a healthy adult and an older adult with sarcopenia.
Photo Source: elderlyfallprevention.com

Picture 2: Battling sarcopenia as a person grows older.
Image Source: i0.wp.com/supplementpolice.com

Photo 3: Maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle is one of the natural remedies for sarcopenia.
Picture Source: www.drdeborahmd.com
The effect of sarcopenia
Sarcopenia causes muscle wasting which could greatly affect the lives of older people. Older people will surely have a hard time performing activities of daily living. Loss of muscle mass and function could increase the likelihood of fall, strip, and other types of accidents.
As you know, fractures are quite difficult to repair in older patients. Sarcopenia also has debilitating effects to the body such as the possibility of having cardiovascular-related diseases and metabolic disorders like diabetes. (2, 3, 4)
Prevalence Rate
In the United Kingdom, 4.6% of men and 7.9% of women 67 years old and above are prone to sarcopenia. In the United States, about 37% of the older adult population have sarcopenia; the average age is 70 years old. (3, 4)
Who is at risk for sarcopenia?
- People who rarely exercise, especially those who have prolonged work at a desk.
- Aging, especially people in their 40 years and up.
- Poorly nourished individuals.
- Those who eat a large quantity of acid producing foods and processed foods. (3, 4, 5)
What causes sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia is commonly caused by a decrease in physical activity, sedentary lifestyle, a significant reduction in the nerve cells that transmit signal to and from the brain telling the muscle to move, abnormally low hormone level, inability of the body to convert protein into energy, and not consuming the daily protein and calorie requirements of the body. (4, 5)
Sarcopenia Symptoms
- Noticeable decrease in muscle size
- Poor balance
- Weakness
- Unsteady gait
- Loss of endurance
- Difficulty climbing the stairs (4, 5, 6)
Sarcopenia Diagnosis
The clinical manifestations of the patient should be carefully observed. Many health care professionals order a dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and a walking speed test to accurately diagnose the condition of the patient. DXA measures the density of the bones.
It is also the very same test used to check for osteoporosis. The doctor might also measure handgrip strength when deemed necessary. (5, 6)
Sarcopenia Treatment
There is no approved drug for sarcopenia but some health care professionals recommend the use of hormone therapy to improve the patient’s muscle mass. Although, there is no exact cure for sarcopenia and the use of hormone therapy is yet to study, there are ways to prevent its onset. (6, 7)
How to prevent Sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia prevention and management include the following:
Exercise regularly
It is just normal to lose muscle mass as you age, but its onset can be delayed if you exercise regularly. Exercising regularly can significantly increase muscle strength, improve your aerobic capacity, and facilitate muscle protein synthesis.
Resistance exercises for at least three to four times a week can help delay the onset of sarcopenia.
Be mindful of what you eat
It is important to choose what you eat, especially as you age. Increase your intake of protein-rich foods as they build and repair muscle fibers. The recommended dietary protein allowance is about 50 grams per day. However, it is not just the amount of protein you eat but the type of protein. Choose your protein wisely. Keep in mind that not all protein are created equal.
Choose a protein that contains essential amino acid, specifically leucine. It is something that the money can’t produce and so it is derived from the protein you eat. Leucine is an amino acid that can be found in the fish, eggs, beef, poultry products, lamb, and milk products.
A small amount of leucine can be found on edible seeds, nuts, and beans. Other essential proteins that should be included in your diet are lentils, whey protein, tuna, salmon, raw cheese, yogurt, and raw milk.
Increase your omega 3 intake
Omega-3 fatty acid can significantly affect the metabolism of muscle protein in older adults. It can help preserve muscle mass, especially when the body is under extreme physiological conditions. To increase your omega-3 acid intake, you have to take fish oil or flax seed oil supplement.
Keep your hormone level balance
Muscle mass can be greatly affected by the levels of hormones in the body. Once you reach 40 years of age, it is important to have your blood work done so as to check the levels of hormones in the body. If there are hormonal imbalances, they can be addressed by taking hormone supplements.
Take supplements that can significantly improve muscle health
- There are supplements that you should include in your day to day life so as to keep your muscle healthy and eventually prevent the early onset of sarcopenia. These include amino acids, vitamin D and calcium, fish oil, and creatinine supplement. Amino acids, especially leucine are good protein while calcium and vitamin D play a vital role in musculoskeletal health.
- Fish oil contains a high level of vitamin D which supports muscle health. Creatinine fuels the muscles during strenuous activities. It works by increasing the muscles phosphocreatine content. In adults, creatinine supplements can greatly help build muscle strength, especially when performing resistance exercise.
- Sarcopenia is a degenerative musculoskeletal condition, which can significantly affect one’s quality of life. While there is no exact cure for sarcopenia, there are many ways to prevent its early onset and to somehow lessen its effect on the body.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, following a healthy and protein-rich diet, exercising regularly, and taking supplements are just some of the ways to prevent the early onset of sarcopenia. If not dealt with accordingly, it could lead to early progression of sarcopenia. If worse comes, sarcopenia could cause you to become bedridden. (6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sarcopenia
- https://www.iofbonehealth.org/what-sarcopenia
- https://draxe.com/sarcopenia/
- https://academic.oup.com/biomedgerontology/article/58/10/M911/534906
- https://www.webmd.com/healthy-aging/guide/sarcopenia-with-aging
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318501.php
- https://www.healthline.com/health/sarcopenia#modal-close
- https://tanita.eu/tanita-academy/for-professionals/what-is-sarcopenia
- https://www.bmj.com/content/341/bmj.c4097
- http://www.lifeextension.com/Magazine/2007/1/report_muscle/Page-01