Subcutaneous Emphysema
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
Dealing with Subcutaneous Emphysema
Subcutaneous emphysema is a medical condition wherein the air gets into the tissues under the skin. It is common in the chest wall area and neck, but can also affect other parts of the body. The air comes from the chest cavity.
It is a bothersome condition for it causes pain in the chest and neck area. Other names for subcutaneous emphysema are subcutaneous air, crepitus, and tissue emphysema. One notices a smooth bulging of the skin that produces unusual crackling sensation when palpated.
Who are at risk for Subcutaneous Emphysema?
It can affect people of any age regardless of the gender or race. There are predisposing factors such as people with facial trauma, respiratory diseases, and those who experienced road traffic accidents.
Causes of Subcutaneous Emphysema
- Forceful vomiting
- Stab wounds
- Gunshot wounds
- Facial bone fracture
- Rib fracture
- Blunt trauma
- Pneumothorax (a condition wherein the lung collapsed because of the presence of air in between the lung and chest wall)
- Whooping cough
- Chemical-related injuries causing burns or corrosion of the esophagus
- A result of medical procedures like bronchoscopy and endoscopy
- Ruptured bronchial tube
- Breathing in cocaine
- Diving injuries
- Dental procedure involving the use of compressed air equipment
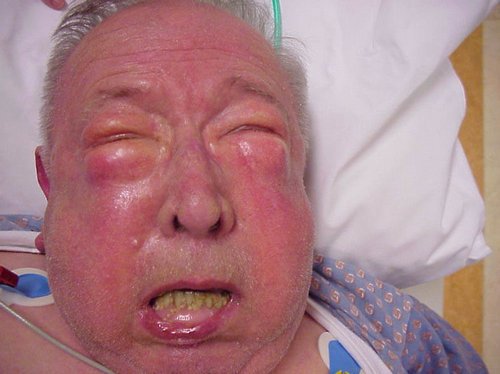
Image 1 : Subcutaneous Emphysema
Picture Source : www.hxbenefit.com
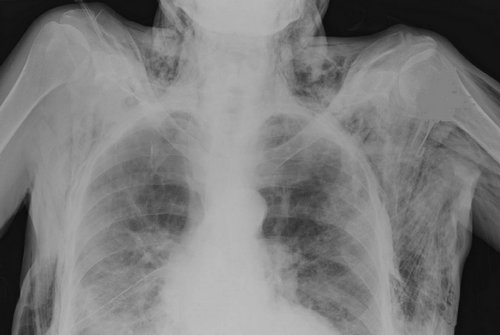
Picture 2 : X-ray of patient with subcutaneous emphysema
Image Source : dxline.info
Signs and Symptoms
- Noticeable swelling and pain in the neck and chest area
- Difficulty swallowing
- Trouble breathing
- Crackling sensation when the affected part is palpated
- Obvious crackles when inhaling and exhaling
- Noticeable change in the voice
When should you see a medical professional?
In normal circumstances, subcutaneous emphysema does not possess any health threat. However, the condition may complicate, especially if the signs and symptoms are not managed properly. Hence, you need to know when to contact your doctor.
- If you suspect subcutaneous emphysema after sustaining an injury, then you have to call 911 and ask for help. Sometimes the infection can get severe and the patient will be required to stay in the hospital for a few days.
- Do not give any fluids to the patient.
- The patient should be immobilized. Moving the patient can cause further injury to the affected part of the body. Move the patient only if he is in a hazardous environment.
How is Subcutaneous Emphysema Diagnosed?
Before any diagnostic procedure is done, there should first be a complete evaluation of the patient’s medical history. A thorough physical examination should also be done to assess for the presence of air bubbles and crackling sounds. The affected part of the body should be inspected for swelling and skin discoloration.
CT scan of the chest
A CT scan of the chest helps in diagnosing subcutaneous emphysema. In the CT scan of the chest, there are visible air pockets. Depending on the condition of the patient, the doctor might order any of the following:
- EKG (electrocardiogram)
- X-ray of the abdomen
- Blood test
- Chest tube
What is the treatment for Subcutaneous Emphysema?
If the patient has subcutaneous emphysema, the medical professional will find out the underlying cause. The doctor will first rule out serious conditions like esophageal perforation, barotrauma cause by mechanical ventilation, diverticulum perforation as a result of intubation, and injury of the trachea and bronchi.
If the subcutaneous emphysema is not cause by the above-mentioned conditions, then it could probably be less serious. Oftentimes, the condition is treated with supportive management. If the cause of subcutaneous emphysema is an underlying infection, then it could probably be due to gas-forming organisms. The doctor will create an incision and debridement of the tissues to thoroughly get rid of the infection.
A subcutaneous emphysema can be due to pneumothorax if the patient is on a ventilator. To manage the condition, the doctor will place bilateral chest tubes. Some doctors insert needles into the emphysematous pocket to release the air. Others insert drains for the air to escape. An infraclavicular incision can also be made to allow the air to escape but this will only be done upon the supervision of experts. If done wrongly, it could result in adverse cosmetic effect in the patient.
The patient might experience breathing problem, especially if the air is large. The treatment management for patients with subcutaneous emphysema complaining of difficulty of breathing is oxygen therapy. The patient is also advised to rest. A complete bed rest and pain medication are required. By giving the patient oxygen, the body will be able to quickly absorb subcutaneous air. Minor cases of subcutaneous emphysema disappears within two days, although majority of the cases resolve within five day period.
The ability of the body to recuperate depends on the root cause of the problem. Typically, the body absorbs the air gradually over a certain period of time. In some cases, a catheter needs to be inserted to release the air.
What is the Prognosis?
What is the chance of survival for patient with subcutaneous emphysema? It depends on the cause and severity of the condition. If the subcutaneous emphysema is caused by diving, then the prognosis is high. In many cases, subcutaneous emphysema resolves on its own. However, the condition can get worst if it involves the heart and lungs. It usually happens to patients with rib fracture. Any fracture in the ribs will affect the protective layer of the lungs. The worst scenario is when the fracture causes air leakage in the subcutaneous tissue of the lungs.
What you should do to prevent Subcutaneous Emphysema?
How can you prevent Subcutaneous Emphysema?
Well, there is no such preventive measures for subcutaneous emphysema. What you must do is be aware of the conditions that can probably cause it. Be wary of the signs and symptoms of subcutaneous emphysema. If you notice the presence of air in the subcutaneous tissues, it should be removed right away.
If the patient has injuries involving the trachea, bronchi, or esophagus, he should be immediately referred to a thoracic surgeon to prevent further complication. If not managed right away, it could lead to death. If the patient is in ventilator and suffered subcutaneous emphysema, bilateral chest tubes should be inserted.
The treatment and management goal is to address the root cause/possible cause of the disease. Proper precautions should be taken the earliest possible time to prevent further complications.
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org
- https://www.symptoma.com
- https://link.springer.com
- https://medlineplus.gov
- https://www.hxbenefit.com
- http://www.dovemed.com
- https://radiopaedia.org
- http://www.nytimes.com
- Subcutaneous Emphysema: Everything You Need to Know about the Disease Including Signs and Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and More by Gaby Alez
- Rosen’s Emergency Medicine – Concepts and Clinical Practice By John Marx, Ron Walls, Robert Hockberger