MPV (Mean platelet volume) Blood Test
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is MPV (Mean platelet volume) in blood test ?
It refers to the size of the platelet, which is used to determine the functionality of platelet.
MPV Blood test is a part of the routine complete blood count (CBC). MPV stands for Mean Platelet Volume. MPV is carefully monitored in patients suffering from a condition related to bone marrow and platelet destruction.
Aside from monitoring the volume of the platelet, other blood markers should also be checked, especially the white blood cells and red blood cells. (1, 2)
MPV Blood Test Range (Normal range)
The normal value of mean platelet volume is expressed in range. The normal range is between 7.2 fL and 11.8 fL in adults. However, reading in between 9.7 fL and 12.8 fL is considered safe too. The normal range varies depending on the laboratory techniques and machines used. (2)
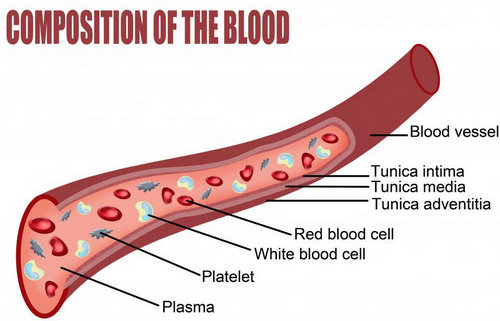
Image 1 : An illustration of blood vessels and various compositions of the blood
Photo source : images.wisegeek.com
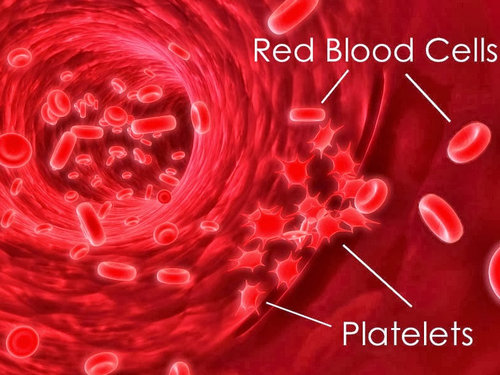 Picture 2 : A microscopic presentation of platelets and red blood cells
Picture 2 : A microscopic presentation of platelets and red blood cells
Photo Source : www.infoinformations.com
What does it mean when your MPV is high?
Platelet plays a huge role in the blood coagulation process. If the level of platelet is high, it could indicate that you are suffering from acute myocardial infarction. In the case of acute ischemic cardiovascular event, the level of platelet is also checked.
To bring the level of MPV to normal range, a person should quit smoking. Health conditions like hypertension and hyperlipidemia should be managed too or else the patient will be at risk for cardiac complications. (2, 3)
What does low mean platelet volume mean?
If the MPV is lower than the normal range, it means that your platelet count is low. If your body does not have adequate level of platelet, it puts you at risk for bleeding. If you sustain an injury, you will be prone to blood loss due to excessive bleeding because the blood does not have enough clotting factor. Low MPV could indicate many diseases and disorders.
A low MPV is an indicator that the platelet in the blood is lower than normal, which puts you at risk for severe blood loss if you get injured. (3, 4,5)
Reasons for low MPV
- Error in collecting blood sample – One of the reasons for low MPV is mistakes in collecting blood samples. Chances are, before the blood is tested it already undergone clotting. This leads to inaccurate result.
- Viral Infection – A low platelet count indicates that you are suffering from viral infection such as Dengue fever and AIDS. (5)
- Side effects of medications – Some drugs lowers MPV such as heparin.
- Genetic disorder/autoimmune disorder – Patients suffering from genetic conditions have low mean platelet volume. Examples are haemolytic disorder, lupus, leukemia, aplastic anemia, and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Over activity of the spleen – A hyperactive spleen can lead to a low mean platelet volume reading.
A very low mean platelet volume is known as thrombocytopenia. Patients suffering from thrombocytopenia are prone to bleeding. It will be extremely difficult for the body to clot the blood during bleeding because of inadequate amount of platelet. (6)
Please note :
Immature platelet fraction normal range and its uses

What does PDW mean in a blood test?
PDW stands for Platelet Distribution Width. It measures the platelet’s uniformity in size. It is significant in determining the functions of the bone marrow. Ideally, younger platelets are large in size. Smaller platelets have been around for several days. If the number of large platelets is high in a patient with a low platelet count, it is an indicator that the bone marrow is now producing sufficient level of platelets.
Platelet Distribution Width is a part of CBC (Complete Blood Count). The doctor will thoroughly check PDW if the patient is suffering from unexplained bruising and excessive bleeding from small wounds and cuts. It is also checked in patients with several episodes of nose bleeding. Purplish spots and rashes are also the reasons for PDW monitoring. (7, 8)
What to keep in mind?
- If the platelet count is low but the mean platelet volume is high, it indicates that there is a destruction in platelet. This is common in patients with immune thrombocytopenia and pre-eclampsia.
- If the platelet count is normal but the mean platelet volume is high, it could indicate chronic myeloid leukemia (over production of a specific type of white blood cells). It could also indicate hyperthyroidism (over production of thyroid hormones).
- A high MPV and high platelet count indicates that the bone marrow is producing too much platelets. (8)
- A low MPV can be caused by a certain types of drugs. These drugs are toxic to the cells and they should be used in moderation.
- Blood clumping is common in people with high mean platelet volume. Since there is excessive production of platelet, there is a tendency that the blood will clump together, which puts the patient at risk for thrombosis, cardiovascular diseases, and stroke. To prevent the blood from clumping, doctors usually prescribe aspirin.
- A low mean platelet volume can put you at risk for bleeding because the clotting factor of the blood is impaired. Hence, a person with low mean platelet should completely avoid aspirin. Giving aspirin could further lead to bleeding. (9)
- Mean platelet volume measures how reactive and large the platelets are. If the mean platelet volume is elevated, it means that the platelet is large and more reactive. This could lead to increased platelet turnover, which will put you at risk for myocardial infarction.
- Mean platelet volume is used as a prognostic marker, especially in conditions like ischemic bowel disease and stroke. By determining the level of MPV, the doctor can tell if the patient has high or low prognosis.
- Cardiovascular factors can greatly affect the level of mean platelet volume. This includes hypertension and excessive smoking. More so, an increased mean platelet volume level can put a patient at risk for thrombosis. It is also linked with cardiovascular disease and cerebrovascular disease. (10)
References:
- http://healthresearchfunding.org
- https://en.wikipedia.org
- https://labtestsonline.org
- www.doctorshealthpress.com
- www.med-health.net
- ehealthhall.com
- www.thrombocyte.com
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- www.brighthub.com
- www.dovemed.com