Cutaneous Horn
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is a Cutaneous Horn?
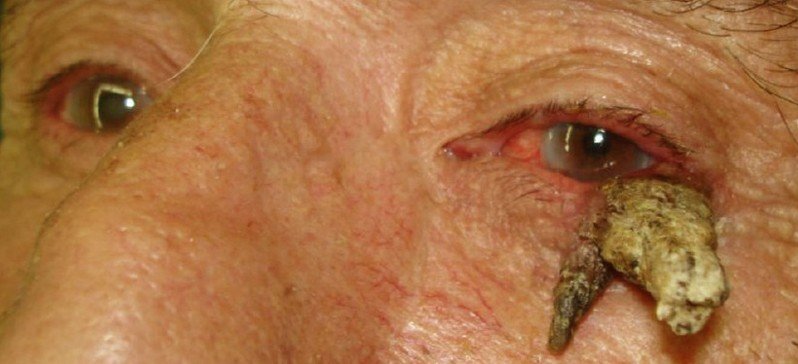
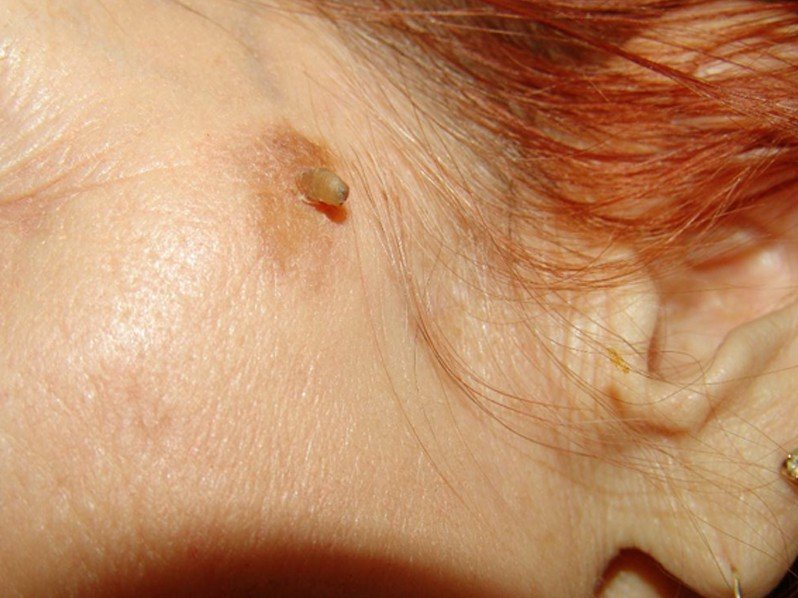
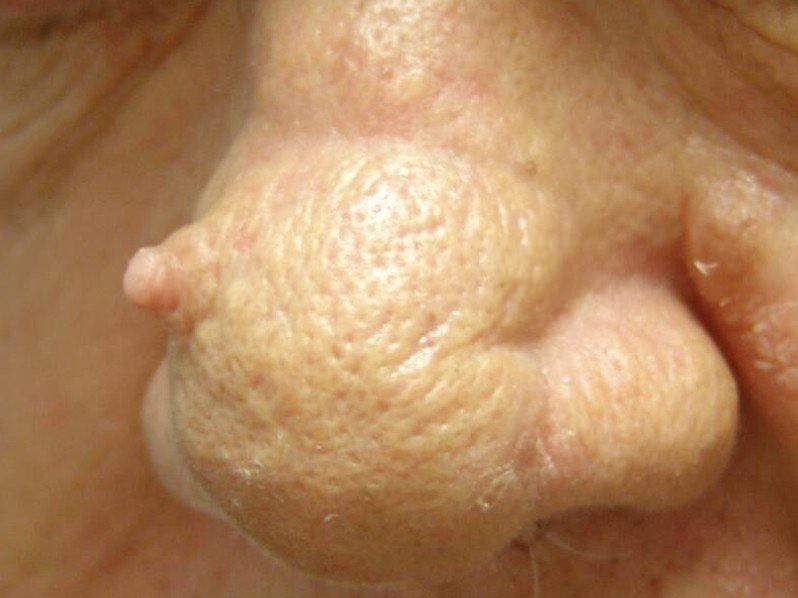
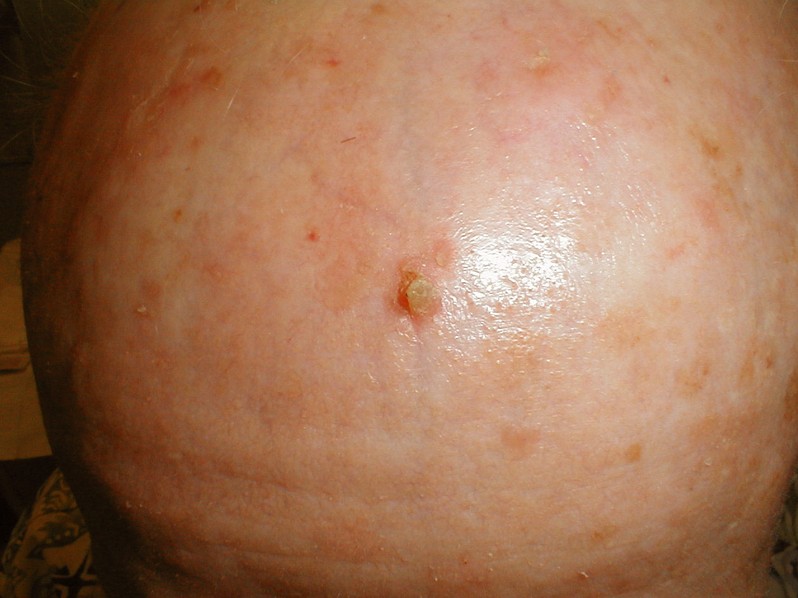
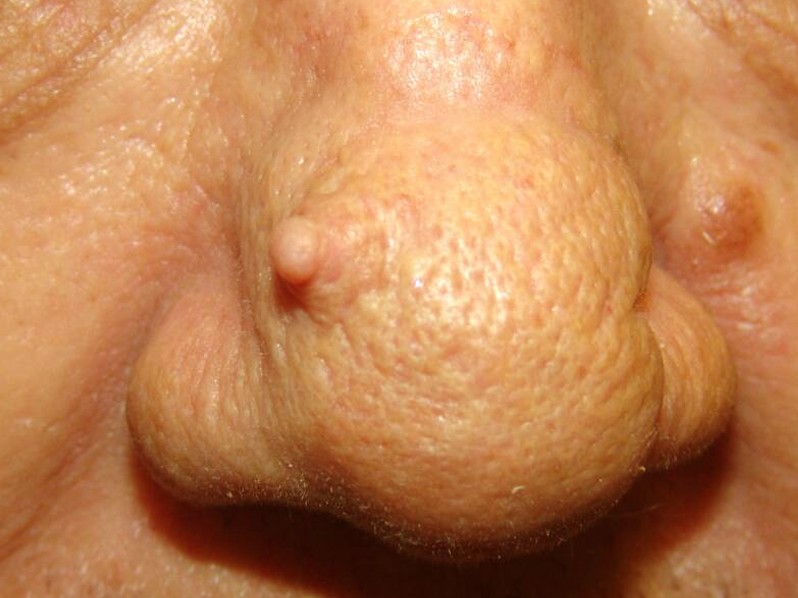
This medical condition refers to the appearance of a skin lesion that is cone-shaped and appears above the surface of your skin and is a rare type of skin growth. It is also called a cornu cutaneum, which is the Latin name for the medical condition. When you look at this lesion it does resemble a small horn, thus giving it its name.
At the base it can be crateriform, flat, or nodular and composed of keratin that is compacted. Although they can affect any age it is most common in older people between the ages of sixty and seventy. It is equally common in both women and men but in men there is a higher risk of this being malignant. It is also more common for people who have fair skin to have a cutaneous horn.
Most of them are curved yellow-brown horns that are hard and can either have a border of skin that is thickened or surrounded by skin that is normal. On the side of the cutaneous horn it can have horizontal ridges that appear terrace-like. Normally the cutaneous horn is taller than twice the width at the base and can vary in size from just a few millimeters to several centimeters.
Many times it is described as feeling and looking like a small animal horn. Usually they will appear singularly but can be multiples and occur anywhere on your body. They are most commonly found on areas that are sun-exposed, especially on the forearms, back of the hands, head, and ears.
They can also develop on the shoulder, penis, chest, and neck. Mostly they are benign but they can be pre-malignant or malignant. Approximately forty percent of these cutaneous horns represent lesions called actinic keratoses, which are pre-cancerous.
Cutaneous Horn Symptoms
There are really no symptoms associated with this medical condition aside from the cone-shaped protuberance that comes out of a bump that varies from red/pink to skin-colored or as a lesion that is flat.
Causes
The exact cause of a cutaneous horn is still not known but what is known is that many of them appear on skin that has been over exposed to the sun. Some believe that being exposed to radiation can trigger a cutaneous horn which is evidenced by a higher rate of cutaneous horns on the hands and feet. These are the areas that are most exposed to sunlight. There have also been cases that some people have cutaneous horns that came from burn scars.
Treatment
If the cutaneous horn is benign usually there is no treatment that needs to be done but you do need to see a dermatologist or physician in order to make sure that it is not pre-cancerous or cancerous. If the cutaneous horns are tender or sensitive at the base they are the ones that will most likely be malignant. If it was benign you need to make sure that you do follow-up visits with your dermatologist or physician to help prevent skin cancer and to make sure that they do not reoccur.
If it was cancerous or pre-cancerous follow-up visits are important also to make sure that they got all the cancerous cells. You should also make sure that you are protecting any areas that are exposed to the sun, especially the area where you had a cutaneous horn removed or treated. You can do this by wearing a hat with a wide brim, wear clothes that cover your legs and arms, and wearing sunglasses. You should also apply sunscreen before you go out in the sun.
Diagnosis
In order to know if the cutaneous horn is benign or not the dermatologist or physician will have a biopsy done. They will surgically remove the horn and do a biopsy on the cells. .
Removal
If the dermatologist or physician finds that the cutaneous horn is either pre-cancerous or cancerous they will want to remove them. The person that removes the cutaneous horn should be either a medical professional that is qualified to remove them or a dermatologist. How they are removed will depend which category they fall into.
Pre-cancerous removal
- It can be frozen with liquid nitrogen and then removed, which is referred to as cryosurgery.
- The cutaneous horn can be scraped and burned, which is referred to as curettage and electrodesiccation.
- By using either a topical medicine that will help to stimulate your immune system or a topical chemotherapy agent, which is an anti-caner medication that will help the cutaneous horn to be removed gradually. If a topical cream is used it can cause a lingering redness but if will fade over time.
Cancerous removal
- Do surgery to remove it
- Radiation therapy
- Doing curettage and electrodesiccation to the cutaneous horn.
- By using either a topical medicine to help simulate your immune system or using a topical chemotherapy agent which is an anti-caner medication that will help the cutaneous horn to be removed gradually. If a topical cream is used it can cause a lingering redness but if will fade over time.
Even if they are benign many people have them removed because they are unsightly. It does need to be removed quickly if it is found to be pre-cancerous or cancerous. One thing that you need to remember is to never attempt to remove the cutaneous horn yourself and the reason is that in order to close the wound where it was you will most likely need stitches. If it was a large cutaneous horn they may need to do skin grafting. When removing a cutaneous horn it can leave a scar.
Cutaneous Horn Pictures
Images, Photos and Pictures collection of Cutaneous Horn…