Microvascular Ischemic Disease
Last reviewed by Dr. Raj MD on January 12th, 2022.
What is microvascular ischemic brain disease?
It is the narrowing of the blood vessels causing a significant reduction of the blood supply to the brain tissues. It is also known as small vessel disease.
It is incidentally picked up in a brain scan such as MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). What does microvascular ischemic changes mean? It means that the tiny blood vessels in the brain are blocked. They are usually filled with clots, but in some instances appear to be ruptured. If left untreated, a part of the brain tissue can die off.
This phenomenon is the same in stroke patients. Usually, the affected area is small that the patient has it unnoticed. Chronic ischemic changes in the brain take some time. Over time, the changes in the neurologic function of the patient gets severe leading to conditions like dementia, memory problems, and neurological issues. (1, 2, 3, 4)
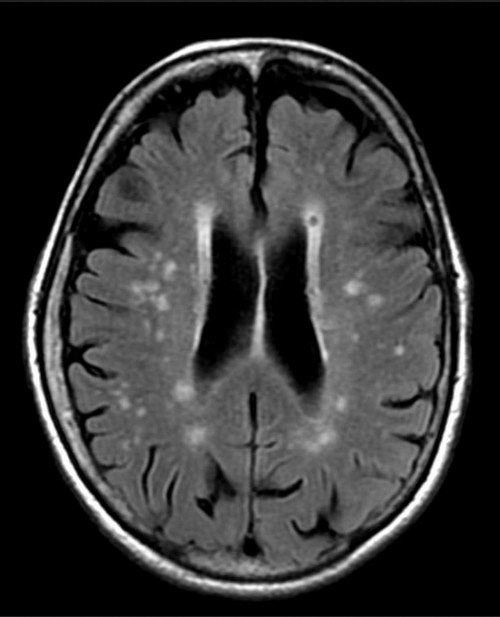
Image 1: A magnetic resonance imaging of the brain showing multiple bright white spots in the tissues of the brain.
Picture Source: www.newhealthadvisor.com
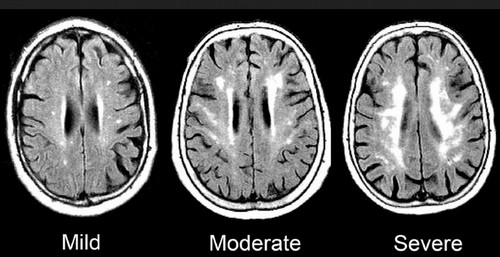
Photo 2: A comparison MRI images of microvascular ischemic disease ranging from mild, moderate, and severe.
Image Source: betterhealthwhileaging.net
Causes of microvascular ischemic disease
- Stress
- Hypercholesterolemia (high level of cholesterol in the blood)
- Excessive alcohol drinking and smoking
- Aging
- Diabetes (high level of sugar in the blood)
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Thrombosis/thromboembolism
- Kidney and heart-related diseases (4, 5)
Symptoms
- Problems remembering things (memory problems)
- Multi-tasking difficulty
- Mood swings (laughing and crying at inappropriate times)
- Weakness on one side of the body
- Personality changes
- Sluggish movement such as trouble walking and muscle rigidity
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Speech problems
- Blurry vision or double vision
- Easy irritability
- Inability to feel and response to sensory stimuli (apathy)
- Uncoordinated movement
- Brain fog
- Frequent falls
- Inability to speak (aphasia) (6)
A generally healthy person can go on the day to day routine without experiencing any symptoms at all. The chronic microvascular ischemic disease symptoms mentioned above are usually felt by people with chronic health issues.
Diagnosing microvascular ischemic white matter disease
A person with strong immune system can have microvascular ischemic disease without demonstrating any symptoms. Most of the time, the condition is undiagnosed. It is only when a person undergoes a scam that microvascular ischemic disease is accidentally discovered.
Usually, brain MRI showed mild chronic microvascular disease. A regular MRI will reveal a homogenous appearance of the brain. If there is bright white spot in the MRI scan, then it could be an indicative of a narrowed blood vessel.
It could also represent blockage in the blood vessel and/or calcification. If there are multiple white spots in the brain, then they are a sign of chronic microvascular ischemic disease.
The doctor will further confirm the diagnosis through an infusion of gadolinium contrast, which will further visualize the spots on MRI scan. The doctor will also assess for behavioural changes and memory impairment. Aside from MRI, the doctor will also perform other diagnostic procedures when deemed necessary.
Examples are stress test with imaging, coronary angiogram, CT scan, PET scan (Positron emission tomography), and endothelial dysfunction test. (6, 7, 8, 9)
Is microvascular ischemic disease fatal? Could there be any possible complications?
Mild microvascular ischemic disease without underlying medical condition is nothing to be alarmed of.
Patients can get by without any clinical manifestations. However, if there are underlying medical conditions, then the doctor should come up with aggressive treatment and management approach. The worrisome underlying medical conditions include kidney-related disease, hypertension, and diabetes.
An uncontrolled blood pressure increases the possibility of stroke. Any changes in the brain should be taken seriously. (8, 9)
If chronic microvascular ischemic disease of the brain is left untreated, it could lead to serious and debilitating health conditions like:
- Stroke – It is caused by an enlarged clot in the brain, which leads to widespread ischemia.
- Dementia – It is most likely to happen if the ischemic portion of the tissue seizes the part of the brain that controls memory. A more serious form of dementia is called Alzheimer’s disease.
- Heart attack – If the clot formed in the small blood vessels around the heart, the muscles in the heart will be damaged leading to heart attack.
- Kidney failure – Kidney failure is most likely to happen if the small vessels in the kidneys get damaged. (1, 4, 5)
How to treat microvascular ischemic disease?
A mild microvascular ischemic disease can be corrected through lifestyle modification. It includes changing the diet of the patient, living a healthy lifestyle, and getting rid of unhealthy habits such as excessive alcohol drinking and smoking.
If there is an underlying medical condition, then the doctor will treat it so as to improve the condition of the patient and prevent further damage. The focus of care includes the following:
- Blood pressure management using blood pressure drugs and cholesterol medications.
- Blood sugar control
- Dietary management focusing on low fat, sugar, and sodium.
- Physical therapy
- The patient will also be given a low dose of aspirin when deemed necessary. (2, 3)
Unfortunately, there is no cure of microvascular ischemic disease. What the doctors do is to treat the underlying medical condition in order to improve the overall health of the patient. Physical therapy can be extremely beneficial to patients too.
The key to improving the patient’s condition is to closely monitor the patient’s health condition. Any changes in the body shouldn’t be taken lightly. Chronic microvascular ischemic disease can be fatal. Hence, patient should receive proper care. (4, 5)
What you can do to prevent microvascular ischemic disease?
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. As much as possible, you should not smoke or even use tobacco products.
- Eat foods that are healthy for the heart and brain.
- Make it a habit to exercise regularly.
- Keep your cholesterol level within normal range.
- Keep your blood pressure in the normal range.
- Use effective stress management techniques.
- Keep your blood sugar level within normal range.
- Maintain a healthy weight. (6, 9)
References:
- http://www.newhealthadvisor.com/Microvascular-Ischemic-Disease.html
- https://www.belmarrahealth.com/understanding-microvascular-ischemic-disease-causes-symptoms-treatment/
- https://www.zocdoc.com/answers/12497/what-is-chronic-microvascular-ischemic-change-of-the-brain
- https://www.med.umich.edu/1info/FHP/practiceguides/cad/IVDBooklet.pdf
- https://www.medhealthdaily.com/microvascular-ischemic-disease/
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/small-vessel-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352123
- http://www.texasheart.org/HIC/HeartDoctor/answer_3313.cfm
- http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ijs.12466/full
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/small-vessel-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20352117